Difficulty Swallowing
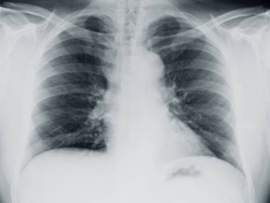
Mesothelioma Symptoms: Dysphagia Regarded as one of the most common mesothelioma symptoms, dysphagia or difficulty swallowing, rapidly progresses in patients stricken with the deadly disease. That being said, several malignant mesothelioma patients will experience that majority of mesothelioma symptoms associated with the disruption of the mesothelial cells. The bulk of mesothelioma symptoms are therefore linked, causing a brutal physiological chain reaction in the human body. Difficulty swallowing or dysphagia is linked to several other symptoms of mesothelioma cancer, including chest pains, abnormal weight loss, anorexia or malnutrition. Difficulty swallowing as it pertains to mesothelioma patients arises from the disruption of the lungs. Dysphagia is most commonly present in those diagnosed with pleural mesothelioma cancer—the most common form of mesothelioma. Because the mesothelium of the lungs is impacted during the profession of the condition, pleural mesothelioma cancer patients have difficulty swallowing and breathing. With an uncommon form of mesothelioma cancer, such as pericardial mesothelioma, the sac surrounding the heart is impacted, augmenting the probability of dysphagia is greatly increased. The likelihood of dysphagia in pleural mesothelioma patients stems from the fact that the area surrounding the heart succumbs to an increased pressure. This increased pressure causes limited oxygen to pass through; patients experiencing this will experience shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing. Peritoneal mesothelioma—a disease that affects the abdomen and other organs, such as the spleen and liver--patients difficulty swallowing may not be present. In most mesothelioma cases, dysphagia is characterized by painful swallowing, which typically progresses to coughing while drinking and eating. Some mesothelioma patients have difficulty swallowing solid foods or liquids, but in some cases, dysphagia will perpetuate difficulty swallowing for both activities. Coughing during eating or drinking may lead to asphyxiation or food particles being digested directly into the lungs. If foods are swallowed, it may be extraordinary painful as it travels to the mesothelioma patient’s stomach. Types of Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing is classified into two types: esophageal dysphagia and oropharyngeal dysphagia. The different types of difficulty swallowing symptoms point to the origin of the symptom rather than how intense the difficulty swallowing is. In most cases, oropharyngeal difficulty swallowing results from neurological, muscular or nerve dysfunctions. For the bulk of mesothelioma patients, esophageal dysphagia is far more likely to be present than oropharyngeal. For the most common form of mesothelioma cancer, pleural mesothelioma, is a mechanical reaction to the proliferation of mesothelioma on the lungs. When dysphagia progresses, patients with pleural mesothelioma cancer may experience choking sensations, as if the food is perpetually stuck in the chest or throat. Typically, when the mesothelioma cancer advances, patients will begin to have difficulty swallowing every time they eat or drink. Eventually, the pressure surrounding the throat and esophagus will be too great, making liquids impossible to swallow. If difficulty swallowing symptoms progress quickly, a mesothelioma patient will likely not be receiving proper nutrition to remain spry. This quick proliferation may eventually lead to malnutrition, abnormal weight loss and dehydration. In more extreme cases, mesothelioma patients will develop horrible bouts of anorexia. Difficulty swallowing is the primary symptom in mesothelioma cancer; however, many mesothelioma suffers will complain about a persistent cough. As the carcinogenesis of mesothelioma progresses, pressure in the abdomen builds perpetuating difficulty breathing. More specifically, expanding mesothelioma cancer places pressure on the esophagus, which further impedes breathing. From this, difficulty breathing leads to difficulty swallowing. Breathing is of course necessary while drinking and eating, and if the lungs are compressing, swallowing becomes extremely difficult. Regardless of form, mesothelioma cancer is a devastating medical condition, which is made worse by its interrelated and progressive symptoms. If a mesothelioma patient is presenting difficulty swallowing symptoms, they must immediately seek medical attention. Progressive dysphagia spawned by a proliferation of mesothelioma cancer will strip the patient from essential nutrients, calories and hydration. This problem will obviously exacerbate all mesothelioma symptoms and lead to a quicker death. What is Mesothelioma Cancer? Malignant mesothelioma is a rare cancer that affects the mesothelial cells located in the serous membranes. The most common form of mesothelioma cancer, known as pleural mesothelioma, damages the lining of the lungs. Roughly 3,000 mesothelioma cases are diagnosed each year. Malignant mesothelioma affects the membranes of several large cavities in the body. These cavities, known as serous cavities, protect several vital organs in the body, including the heart and lungs. The membranes surrounding these cavities defend some of the body’s organs from abrasions that that arise from everyday movement, such as breathing. The serous membranes originate from mesothelial cells, which form to create the mesothelium—protective tissues of the serous membranes. Malignant Mesothelioma cancer is categorized in the following forms: Pericardial Mesothelioma: Originates in the lining of tissue surrounding the heart (pericardium). Peritoneal Mesothelioma: Originates in the membrane surrounding the abdomen (peritoneum). This is a rare cancer that may also disturb the testicles, more specifically the tissues surrounding the scrotum. Pleural Mesothelioma: The most common form of mesothelioma cancer which disrupts the lining of the lung cavity. All mesothelioma cancers derive from acute tumors and then spreads to surrounding organs and tissue. The bulk of mesothelioma cases stem from asbestos exposure. When detected, mesothelioma cancer is often found in its latter stages. This delayed finding makes prognosis exceptionally pessimistic. The average survival time of mesothelioma cancer is only 1 to 2 years. This timeframe; however, fluctuates on the type of mesothelioma cancer and the general health of the patient. Mesothelioma cancer is nearly impossible to accurately diagnose because the symptoms are inconspicuous. Malignant mesothelioma cancer sufferers do not observe mesothelioma symptoms for 10-15 years following infection. Furthermore, complications from a delayed diagnosis originate from the cellular makeup of mesothelioma cancer—mesothelioma is nearly impossible to differentiate from basic cancers.