MRI Scan
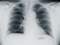
Mesothelioma Diagnosis: MRI Scan Mesothelioma is a rare cancer that develops from the mutation of cells in the mesothelium—the protective lining of several internal organs. Mesothelioma cancer is primarily caused by prolonged exposure to asbestos. Asbestos, when contacted, propels cancerous filaments into the air. These filaments, over a period of time, stick to the mesothelium. Over time, cancerous tumors form, which have the potential to rapidly metastasize. The bulk of mesothelioma patients, therefore, were at some point, previously employed in industries that utilized asbestos or worked with the fiber in some capacity. Although there are several forms of mesothelioma cancer, the majority of cases develop in the internal wall of the chest cavity or the lining of the lungs. Common symptoms attached to mesothelioma will include: shortness of breath, stemming from a build-up of fluid between the abdomen and lungs, weight loss and painful coughing. One of the primary characteristics—and the major reason why the disease is so deadly—stems from its relatively innocuous symptoms. Mesothelioma cancer is nearly impossible to detect in their early stages. The difficulty attached to diagnosing mesothelioma stems from the condition’s dormant symptoms. A mesothelioma patient will often notice symptoms 15-20 years after the initial infection takes place. Similar to other forms of cancer, mesothelioma is categorized by stage. As the disease shifts through stages, mesothelioma cancer becomes more deadly. This insidious nature is paired with mesothelioma’s inconspicuousness to create a deadly disease. Mesothelioma patients typically die within 6 months to 1 year of diagnosis. Frequently, mesothelioma cancers will not be diagnosed until the tumors metastasize to the vital organs of the body (such as the heart or lungs). When mesothelioma reaches stage III or stage IV it is ruled inoperable. If mesothelioma cancer, by chance, is caught before the disease spreads, curable treatments, such as surgery, may be suggested to extract the malignant tumors. Furthermore, a number of palliative surgeries are administered to mitigate the suffering associated with mesothelioma cancer. If you have worked with asbestos in the past you should contact your medical professional to set-up a physical examination. You should schedule this appointment if you feel healthy or do not notice any symptoms. Upon evaluation, the medical professional may opt to have an MRI. These images will be requested if the doctor believes that you may be susceptible to mesothelioma cancer. The MRI is an essential tool for diagnosing mesothelioma cancer. What is an MRI? An MRI (also known as a magnetic resonance imaging device) is a form of imaging technology which involves the use of magnets that are able to generate images of the interior structures of the human body. This scan is extremely useful for evaluating soft tissues and diagnosing medical conditions, like malignant mesothelioma cancer. An MRI works because the images are generated through the scanner, which is an advanced machine that utilizes magnets to form a magnetic field. The field excites the protons that that are located within the water molecules of the human body. These protons are aligned within the magnetic field and are then pushed by a complimentary magnetic field so that they are no longer aligned. When the protons realign within the field, they generate radiofrequency which are used to produce the image. Following this, multiple agents are used to increase the signal so that the MRI image can be excessively detailed. Diagnosing Mesothelioma Cancer from an MRI: Similar to a CT scan, an MRI is an image-based scan that is far superior to x-rays. The supremacy of an MRI scan is found in its ability to see the internal tissue of the targeted area. Images generated from an MRI and CT scan may be similar; however, the MRI is more effective in visualizing the contrast of soft tissue. This means that an MRI can reveal the tiniest of variations between similar structures in soft tissue alignments and between different parts of a structure. When compared to other imaging devices, a CT scan is typically the opening scan, used to determine whether a person has mesothelioma cancer. In contrast, an MRI provides medical professionals with more detailed visualizations of the tissue. As a result of this specialty, an MRI is used when a CT scan is not conclusive. One of the primary uses of an MRI is for the staging and planning of mesothelioma surgeries. Medical professionals will utilize an MRI in order to determine how mesothelioma cancer has progressed and spread to the surrounding tissues so that mesothelioma surgery can be properly planned. Another difference between MRI and CT scans is found in the long-terms risks of the imaging tests. CT scans use ionizing radiation techniques that are known to damage the tissues of the human body. In contrast, an MRI will use magnetism, which does not have any documented risk factors on patients.