Peritoneal Mesothelioma
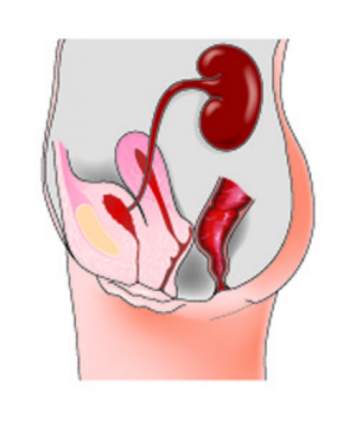
Peritoneal mesothelioma is a form of cancer which is caused due to the overexposure or prolonged exposure to asbestos. One of the four known types of mesothelioma, peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the lining of the abdominal cavity, known as the peritoneum.
Symptoms of Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal is the second most common type of mesothelioma, accounting for nearly 30% of all mesothelioma cases. The symptoms associated with this rare form of cancer are caused as the result of fluid buildup between membranes and tissues in the peritoneum and surrounding organs.
This causes for pressure to form and be exerted on the internal organs and the abdominal region, essentially restricting the proper functioning of such organs. Among the involved symptoms, some may include:
1. Abdominal pain
2. Abdominal swelling
3. Sudden or unexplained weight loss
4. Nausea
5. Vomiting
6. Fatigue
7. Anemia
8. Fever
9. Night sweats
10. The formation of lumps in the skin around the abdominal area
Because peritoneal mesothelioma has the possibility of metastasizing to other parts of the body, other symptoms may also be experienced. In such a case, common symptoms may include trouble swallowing, and the swelling of the face and/or neck.
Symptoms, though may prove of worth in the overall diagnosis of the disease, are also unreliable due to the fact that they are not present on an immediate basis. Most patients with peritoneal mesothelioma will not experience or exhibit symptoms until decades later after the initial exposure to asbestos, the leading cause for this kind of cancer.
Diagnosis of Peritoneal Mesothelioma
The appearance of symptoms will prove not to be an accurate or determinative factor in diagnosing peritoneal mesothelioma. Many of the symptoms exhibited by patients will resemble those caused by other health conditions and illnesses, making the reliance of symptoms alone not a conclusive diagnostic marker.
The most effective diagnosis procedures in finding peritoneal mesothelioma will be a CT scan and a biopsy. A CT scan can help localize any tumors present in the peritoneum or the presence of excess fluid. Upon finding such abnormalities, a biopsy of the affected tissue will be necessary in order conclusively determine the presence of peritoneal mesothelioma.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Treatments
Unfortunately, medical research and studies have yet to develop an actual cure for peritoneal mesothelioma. Therefore, the treatment options for the disease will concentrate on reducing the associated symptoms and limiting the possibility of the cancer spreading to other organs in the body.
The most common types of mesothelioma treatments will involve surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation, with the three methods often being combined to combat the disease. However, the viability of existing peritoneal mesothelioma treatments will be limited by the overall prognosis of the disease.
Because this kind of cancer is often times not detected until the later stages, it is not uncommon for surgery not to be an option for many patients. This occurs particularly in the case where the tumor has grown to a large size or has spread to other parts of the body. The overall health of the patient will also play a factor, particularly if the patient is considered too weak to undergo and recover from surgery.
In general, peritoneal mesothelioma treatments are employed for the purpose of extending the life expectancy of the patient.
NEXT: Pleural Mesothelioma